Description
In 2019, Collège Boréal established an applied research sector to meet the economic, industrial, and social needs emerging in the communities it serves.
What is applied research?
Applied research is used to find practical solutions to concrete challenges. To do so, it uses the latest technologies and discoveries to create new products, services, and processes or to improve current practices and products.
Our services
Services offered to our partners
- Support and guidance in project development, including the development of funding applications and receiving ethical approval when necessary
- Identification of sources of funding and administrative management of projects, agreements, and reports
- Prototyping and concept validation
- Creation and sharing of tools and resources
- Access to the expertise of our highly qualified researchers
- Support from our students in your projects supervised by our researchers
- Access to our research and innovation facilities and to our state-of-the-art equipment
Services offered to school staff
- Support and guidance in the development of funding applications and ethical evaluation requests
- Identification of funding source and administrative management of partnerships, projects, agreements, and reports
- Support for multidisciplinary collaboration initiatives and research partnerships
- Access to research and innovation facilities and state-of-the-art equipment
- Opportunities for internships, summer jobs, and part-time jobs for your students
Image Gallery







Current Projects
Project Manager: Frédéric Boulanger
Student Research Assistants: Diane Richer, Nathalie Kalinga
Partner Organizations: Association socioculturelle de la communauté rwandaise de Windsor, Burundian Community of Windsor and Congolese Community of Windsor-Essex
Granting Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: April 2020 to April 2024
This project seeks to evaluate, improve and innovate upon the model of integrated service delivery to newcomers in collaboration with the Association socioculturelle de la communauté rwandaise de Windsor, the Burundian Community of Windsor and the Congolese Community of Windsor-Essex. Newcomers are important players in the country’s economic growth, as well as one of the main drivers for mitigating the impacts of labour shortages, an aging population and the country’s overall declining birth rate. Settlement and integration services are essential to addressing their diverse needs.
The newcomer community in Windsor-Essex is looking for effective and compassionate services and supports that will facilitate and accelerate the socio-economic integration of newcomers. In order to address these needs, the research team will compare the trajectories of newcomers who (1) have made little or no use of settlement services, (2) have used settlement services offered by a federally funded service provider, and (3) have an economic integration plan, have had a socio-economic integration plan, or are in the process of developing their socio-economic integration plan. Using a mixed-methods approach, the research team will collect qualitative data through interviews and focus groups, as well as quantitative data on the progression of language skills, the transition to post-secondary education, and the average wage of newcomers.
Anticipated outcomes of this project include the development of a proven intervention model that can be adopted or adapted by other service providers, and the creation of a newcomer recruitment and retention model for small and medium-sized municipalities.
Click here to view the preliminary results report.
Key Words: Newcomers, Socioeconomic Integration, Settlement Services, Intervention Model
Project Lead: Camille Lemieux, Donald Perreault
Partner Organization: Ontario Association of Cemetery and Funeral Professionals
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: May 2021 to May 2023
The COVID-19 outbreak in Canada has led provinces and territories to institute new regulations around funeral activities, limiting the size of gatherings and restricting memorial ceremonies. In Ontario, many places of worship, including churches, mosques and synagogues, have been temporarily closed because of physical distancing requirements. In addition, The Bereavement Authority of Ontario has instituted new directives which restricts the number of people who can be at a funeral service, whether inside a funeral home or outside at a cemetery, to 101. These restrictions are having a dramatic impact on the ways in which individuals and families grieve, limiting access to funeral services, and increasing the demand for immediate cremation without ceremonies2. The effects of COVID-19 are also impacting bereavement professionals, a group that is often overlooked as essential or “frontline”. Many of these “last responders” are experiencing heightened levels of compassion fatigue and vicarious trauma because of the disruption of industry norms and practices that have become impersonal and “deritualized”. Additional workplace stresses resulting from inconsistent access to personal protective equipment and increased hygiene and cleaning requirements have also contributed to diminished mental health and well-being among bereavement professionals, who are already at heightened risk of alcoholism, drug abuse, suicide and PTSD3. To address the emerging and compounding negative impacts of COVID-19 on the mental health of bereavement professionals, The Ontario Association of Cemetery and Funeral Professionals (OACFP herein) recently launched the Action for Mental Health: Be Brave initiative, a five-part video series aimed at promoting positive mental health among bereavement professionals. The objective of this collaboration between Collège Boréal, the OACFP is to develop additional bilingual mental health and educational resources, including a province-wide virtual peer support network to support the on-going mental health and wellbeing of bereavement sector professionals.
Project Lead: Marc Hébert
Partner Organization: Northern Ontario Farm Innovation Alliance, University of Guelph, University of Manitoba
Funding Agency: Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Farms and Rurals Affairs
Duration: May 2022 to May 2024

The purpose of this study is to explore the value of the three sisters to soil fertility, plant health and productivity, and insect communities.
Project Lead: Marc Hébert
Partner Organization: Pelletec Canada
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: 6 months
Soil pollution from mining activity can lead to the depletion of soil nutrients and cause accelerated soil acidification. For over a century, the most common practice of reducing soil acidity involved the use of dolomitic lime. One alternative treatment to liming is the use of wood ash, a natural by-product that can not only increase soil pH but also reduce the need to apply artificial fertilizers. However, wood-ash field application has many challenges due to its powdery form; the fine particle of the ash makes it volatile and easily carried away by wind and runoff, varying particle sizes creates challenges to uniform application, and fine particles can be inhaled and cause health issues. Pelletec Canada (Pelletec herein), a forest industry company located in New Liskeard, Ontario, is exploring pelletizing or granulating wood ash as a solution, but studies are limited on the agglomeration of a hydrophobic powder such as wood ash. Therefore, the objective of the new partnership between Collège Boréal and Pelletec is to conduct a feasibility study on the agglomeration of wood ash into granules or pellets for soil application purposes. The success of the study will lead to a new type of soil rehabilitation amendment and provide Pelletec with a new product.
Project Leads: Johnny, Kashama Batabela, Jean Pierre Kapongo, Marc Hébert
Partner Organization: Northern Wildflowers
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: 6 months
Wildflower plantings have become increasingly more apparent and important for supporting biodiversity in impoverished landscapes, parks, golf course roughs, and seed production farms. Wildflowers are typically planted as seed mixes and a nurse crop is recommended. Cover or nurse crops help stabilize erodible sites and reduce aggressive weed encroachment. Current practices focus on the use of ryegrass as a nurse crop. In the past year, Northern Wildflowers, a wildflower seed producer located in Whitefish, Ontario has encountered several challenges with the use of ryegrass as a nurse crop in their seed mixes: ryegrass is not easily procured in Northern Ontario, it competes with native grasses, and it can also compete with the native wildflowers. The company would like to explore alternative nurse crops that will be easily procured in their region and that do not compete with native plants, but studies on such alternative are limited. Therefore, the objective of the new partnership between Collège Boréal and Northern Wildflowers is to test the effectiveness of various novel nurse crops in supporting the germination and survival of native seeds to develop a new seed mix recipe for Northern Wildflowers. The results of the study will provide Northern Wildflowers with a product that will increase biodiversity and ecosystem services while increasing their efficiency.
Project Lead: Jean Pierre Kapongo
Partner Organization: TECC Agriculture Ltd.
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: May 2022 to May 2024
Over the past several decades, oat production has significantly declined in Ontario, in part due to heavy aphid infestations that reduce crop yield and spread virus (e.g., barley yellow dwarf virus). Heavy pesticide application is commonly used to manage infestation despite the associated negative environmental impacts. TECC Agriculture Ltd. requires support to develop a new highly effective and environmentally friendly pest control for oat producers in Northern Ontario. Therefore, this project will evaluate new cultural and biological pest management techniques to identify the most efficient and environmentally friendly pest control strategy for farmers in Northeastern Ontario.
Project Lead: Jean Pierre Kapongo
Partner Organization: Leisure Farms
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: May 2022 to May 2024
Cylamen mite (Phytonemus pallidus) is an emerging strawberry pest that stunts plant growth and fruit development. Controlling the pest has proven challenging as it is hidden during its feeding behaviour, consequently making pesticide application less effective.In recent years, Leisure Farms has been facing increasing Cylamen mite infestations in their strawberry crops, thus reducing crop quality and yield. The farm requires support to address the emerging pest infestations in order to limit revenue loss caused by the Cylamen mite. Therefore, the objectives of this study are 1) to determine the threshold level of the Cylamen mite in Northern Ontario and 2) to determine an environmentally friendly control method that will keep the mite population below threshold level while maintaining biodiversity in affected regions.
Project Manager: Marc Hébert
Student Research Assistants: Alexandre Roy-Guay, Fateh Anabi, Chantal Frescura, Olivia Baudet, Valérie Poisson
Partner Organizations: Glencore Sudbury INO, Atlantic Power Generation
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: April 2019 to June 2023
In Sudbury, Ontario, the release of vast amounts of sulfur dioxide and metals generated from over a century of mining activities has led to the depletion of soil nutrients and accelerated soil acidification. Concerted efforts since the 70s to reduce soil acidity in the region with dolomitic lime have taken place, but the Sudbury Soil Study (2009) showed that low soil fertility, poor nutrient balance, and limited capacity for water retention remained, especially near mining properties. While dolomitic lime lowers acidity levels, it provides little nutritional value for the soil and vegetation meaning that artificial fertilizers must be used to render the soil fertile for any immediate planting.
In this project, the research team is examining the viability of using a wood ash treatment for the purpose of soil remediation on acidified soils resulting from smelting operations; wood ash can not only increase soil pH but also reduce the need to apply artificial fertilizers. Atlantic Power Generation (APG) operates a biomass generation facility on the north side of Highway 11 that produces waste heat from the combustion of wood waste in a boiler. The research team is studying the viability of using this residual wood ash, which would otherwise be disposed of in a dedicated landfill, for mine-site soil remediation by conducting field trials on Glencore Sudbury INO land.
The results could provide Glencore with an inexpensive and environmentally friendly alternative to liming and fertilizing, and reduce APG’s landfill output.
Key Words: Soil Acidification, Soil Depletion, Soil Remediation, Soil Nutrients, Mining Activity
Project Lead: Marc Hébert, Marc Nellis
Project Team: Roch Rochon, Olivia Baudet, Nathan Basiliko, PhD (Laurentian University), Graeme Spiers, PhD (Laurentian University), Peter Beckett, PhD (Laurentian University), Jonathan Lavigne, PhD Candidate (Laurentian University)
Student Research Assistants: Brady Chisholm, Danny-Elle Henri
Partner Organization: Laurentian University, The Ontario Aggregate Resources Corporation (TOARC), Ethier Sand & Gravel, and Pioneer Construction, Glencore
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: May 2021 to May 2024
Numerous “legacy” pit and quarry sites exist here in Northeastern Ontario that date from prior to the province’s 1990 Aggregate Resources Act, which now universally requires progressive rehabilitation for all permitted sites. Some of these legacy sites, identified by the project partner, The Ontario Aggregate Resource Corporation, will be used in the study. Protocols we will developed will focus on low-cost solutions that improve the long-term rehabilitation trajectories and a broad range of ecosystem services. Ultimately, it will make the aggregate-production and mining sectors more financially competitive and earn them stronger environmental and social license to operate.
This project will address the limitations to plant restoration and biodiversity in Northeastern Ontario aggregate sites. The Collège Boréal-Laurentian University research team will explore novel soil amendments and planting strategies to facilitate restoration of biodiversity and key ecosystem functions like nutrient cycling, carbon storage, resilience to disturbance, and protection of ground and surface waters. A key goal is also to contribute protocols that can be commercially applied further in the aggregate- production and other mineral mining sectors that manage waste rock as part of their operations towards progressive and final closure and site restoration.
Project Lead: Johnny Kashama Batabela
Partner Organization: Leisure Farms; Rocha Farm; Adagio Farm; Truly Northern Farm; Rubber Boot Farm
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: May 2022 to May 2024
Ethnic vegetables are defined as vegetables that are not traditionally grown in Canada but are imported. Growing and selling specialty crops or new value-added products can attract new customers and increase the income of agri-businesses. The project partners are looking for support to develop growing protocols for a variety of ethnic vegetables that will be specific to Northern Ontario. Therefore, the study aims to (1) measure the adaptability of various ethnic vegetables to Northern Ontario, (2) determine the yield and gather measurement of profitability compared to other local crops and (3) demonstrate their potential as new alternative vegetables.
Image Gallery








Completed Projects
Project Lead: Denis Ouimette
Student Research Assistants: Jérémie Roy, Alex Létourneau and Danika Courchesne
Partner Organization: Construction La Ray
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: April 2020 to March 2021
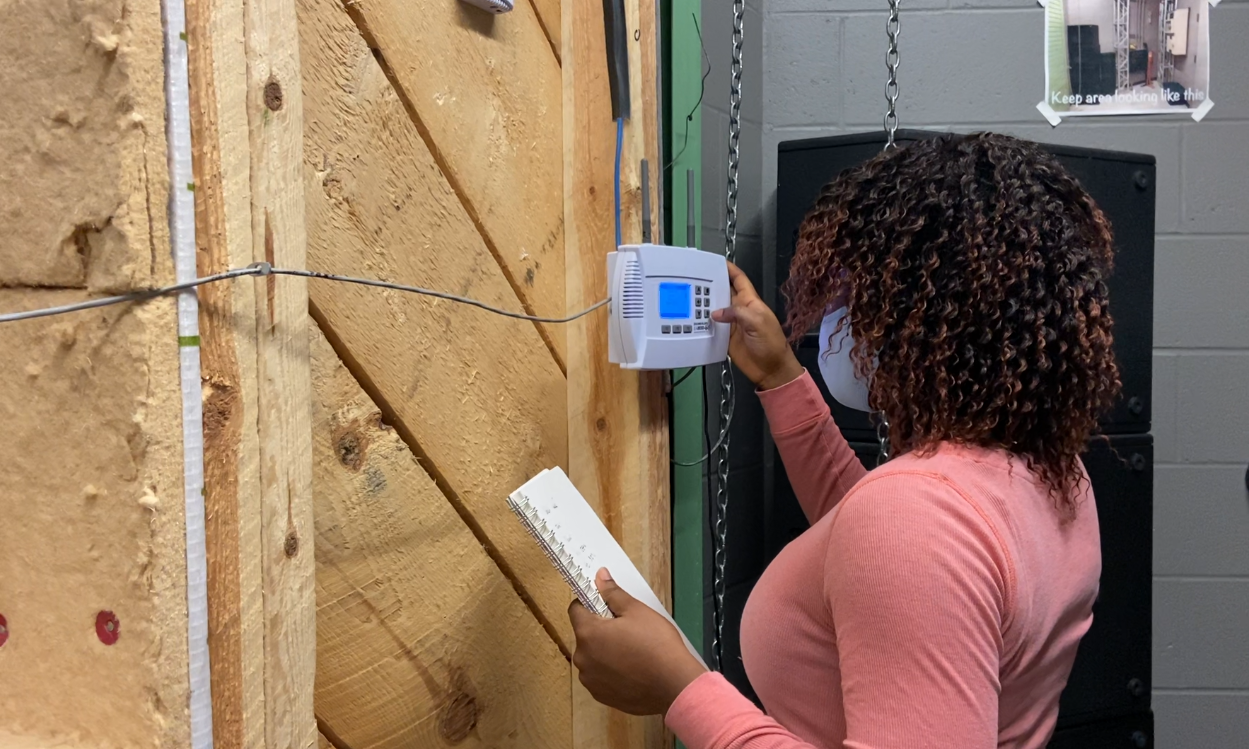
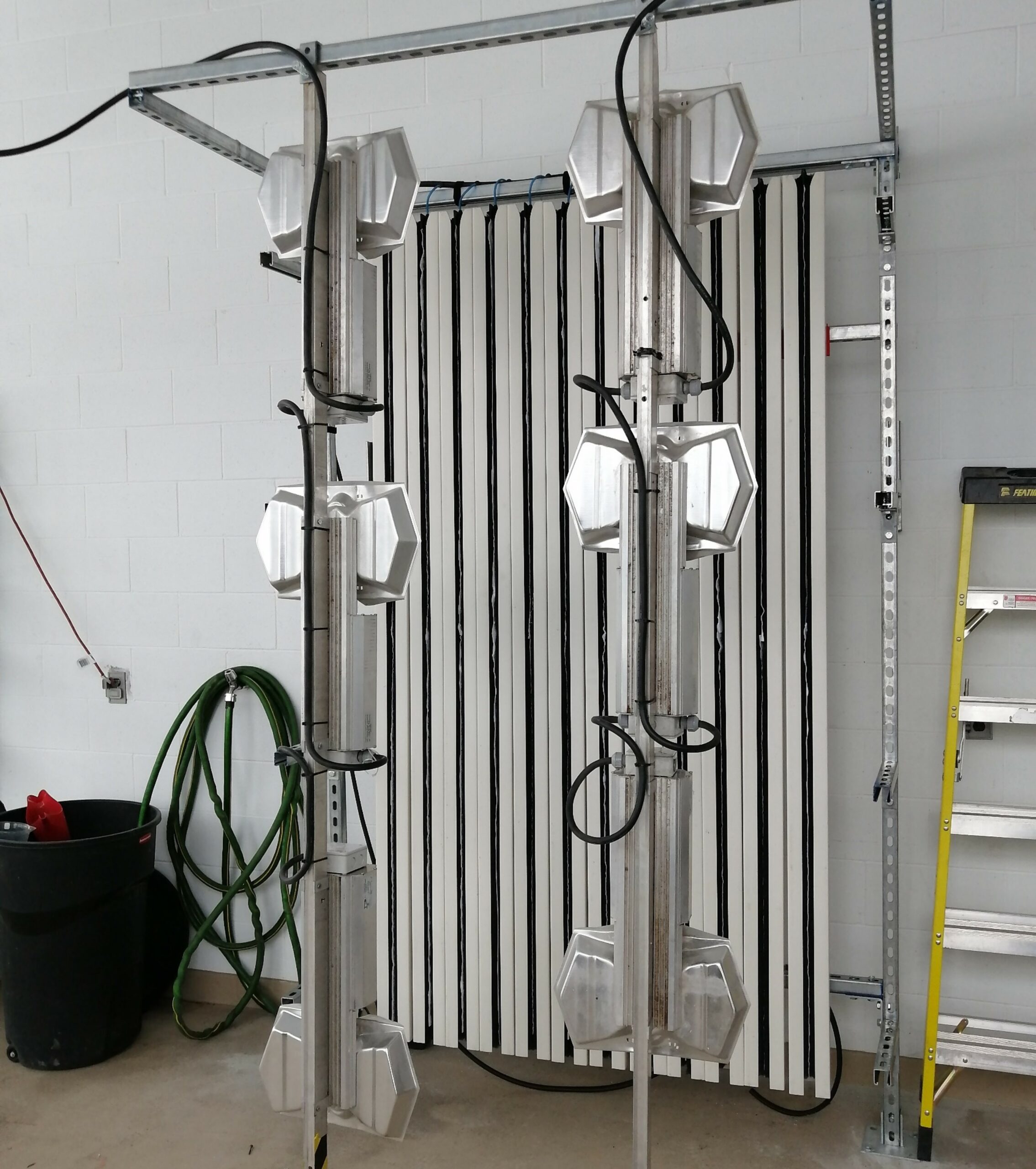
Despite advances in green building construction, windows are still a major source of energy loss. As part of this research project, Collège Boréal collaborated with the company Construction La Ray on a feasibility study for the potential development of a new product that would improve the energy conservation performance of windows that the company could then use in its residential, commercial and industrial construction projects. The main objective of the research project was to develop a new product that would help reduce the carbon footprint of Canadian infrastructure, while meeting construction industry standards. To do this, the research team developed and built a wall with a window and different energy components: an exterior wood finish, open joists, cellulose insulation, wood-based insulation, a rigid insulation board of plywood and a waterproof varnish. Next, the team installed systems to collect data on humidity, temperature, etc., and detect leaks and air infiltration. Infrared photos were also taken several times a day and a week.
The analysis of the data collected will help determine whether it is possible to develop a new product for market entry that will reduce the loss or gain of energy from windows, thereby improving the energy consumption of infrastructure and its associated costs.
Key Words: Green construction, Green infrastructure, Energy performance, Feasibility study, Energy conservation, Market entry
Project Lead: Kuny Laurin
Student Research Assistant: Jaden Laplante
Partner Organization: Gagnon Renewable Resources Inc.
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: September 2021 to March 2022
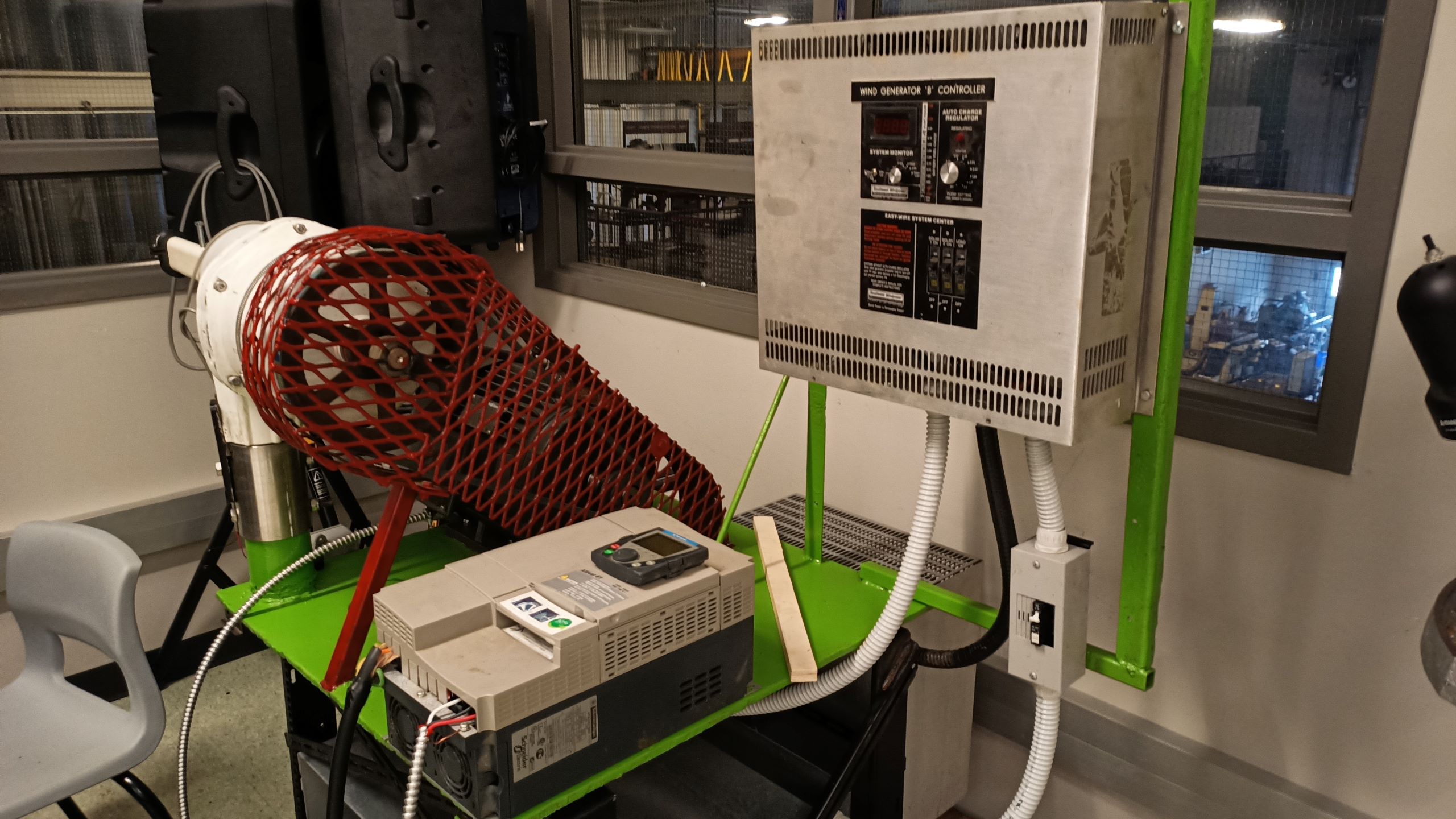
In the context of current greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction and climate change mitigation goals, wind energy has received increasing attention worldwide, with technologies developed and used globally. To maintain the industry growth, innovative technologies must keep evolving, focusing on improving reliability, increasing capacity factors, and reducing costs. However, despite the rapid evolution of wind technology, high-performance system parts such as sensors and controllers are still flawed and lack selection. Gagnon Renewable Resources Inc. (GRR herein) has been unable to source a controller that fits the needs of their new wind turbine, and thus, the company aims to develop a new innovative controller that will meet their requirements. Therefore, the objective of the new partnership between Collège Boréal and GRR is to conduct a product development and proof of concept study of a new innovative wind turbine controller. If the study is successful, GRR will have a new cutting-edge device to carry forward their new wind turbine system. This new system will contribute to the economic development of the company and will allow them to approach clients and present them with clean energy options for their electricity needs.
Project Lead: Guy Lachapelle
Student Research Assistant: Abdelaziz Chihi
Research Technologist: Jenna Butler
Partner Organizations: DHL Machine Work
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: June 2020 to March 2021
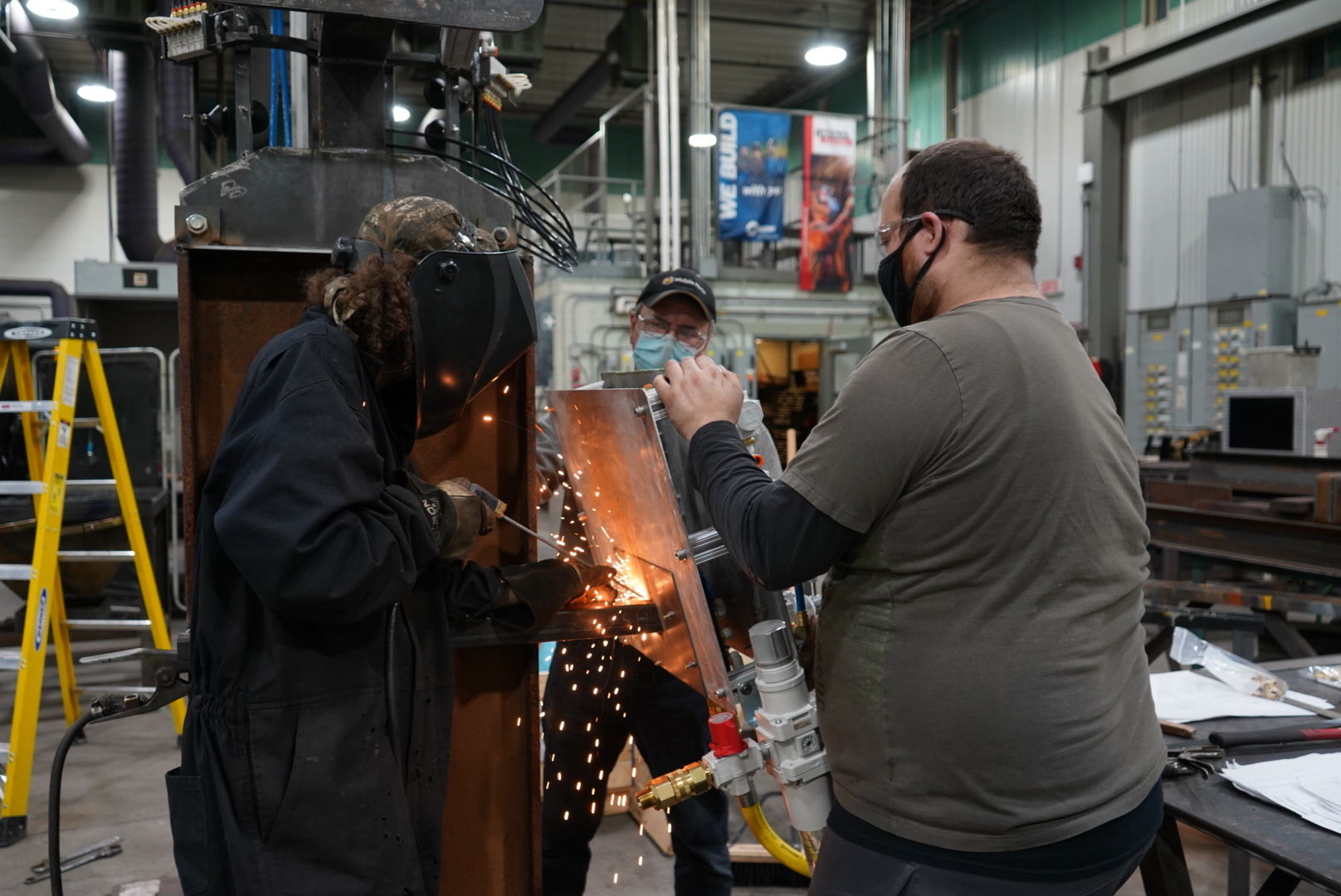
In mining and mineral processing facilities, core is studied, cut, sampled and stored in core storage racks made of wood and steel. Over time, the combination of these various activities and the combined weight of all the core compromises the integrity of the core storage racks. Additional damage to the core racks is caused by various environmental and weather conditions since they are often stored outside. Deformation of the steel rungs and cracks or splits to the wooden frame can potentially lead to a collapse, a significant safety issue. Further, ergonomic research on the structural features of the core racks by the Centre for Research in Occupational Health and Safety at Laurentian University determined that some of the rungs may be contributing to higher levels of musculoskeletal disease among workers.
To address these safety and ergonomic issues, the research team at Collège Boréal collaborated with DHL Machine Work on the construction and evaluation of an enhanced core storage rack prototype with the goal of commercializing the new prototype to Canada’s mining exploration and processing sectors. To start, they designed and illustrated diagrams of a new core storage rack, including material, dimensions, and sectional views. The research team constructed a prototype at Collège Boréal which was transported to the core processing facility in Sudbury for a three-month testing period.
Key Words: Core, Core rack, Mining, Mineral processing, Prototype, Commercialization, Workplace health and safety
Project Manager: André Ferron, Roch Rochon
Student Research Assistants: Olivia Baudet, Nicholas Isabelle, Claire Binette, Brianna Gervais, Emma Maurice, Danny-Elle Henri
Partner Organizations: New North Fisheries
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: April 2019 to June 2022
In Canada, aquaculture is an $840 million industry of which Ontario accounts for less than $20 million. Rainbow Trout is the major fish species produced through commercial aquaculture in Ontario, but Lake Whitefish is the most important species captured through commercial fishery activities in the Great Lakes. For decades, the Great Lakes ecosystems have been negatively impacted by the appearance of several invasive species such as the zebra mussel, and catches of lake whitefish have decreased while demand has increased.
To help address this demand, the research team, in collaboration with New North Fisheries, is studying cage culture of Lake Whitefish as a possible solution. Each year, for three years, a new generation of Lake Whitefish eggs will be collected from Lake Huron and incubated at Collège Boréal in the fall to produce fingerlings that will be transported to a cage in Lake Huron the following summer. They will then be raised in the cage until market size. Throughout, the research team will collect and analyze culture data according to the Cage Culture Guidelines of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry. With this study, we will be able to ascertain the feasibility of raising Lake Whitefish from egg to adults for commercial purposes.
Key Words: Lake Whitefish, Aquaculture, Fingerlings, Cage Culture, Great Lakes, Commercial Fishery
Project Managers: Dr. Jean Pierre Kapongo and Josée Côté
Student Research Assistants: Cora Long et Kaelyn Charron
Partner Organization: BioNorth Solutions
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: July 2020 to December 2020
Natural plant growth promoters (PGPs) are promising sustainable technological innovations that can enhance flowering, plant growth, fruit set, crop productivity and nutrient use efficiency, and tolerance against a wide range of abiotic stressors, consequently reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers. BioNorth Solutions manufactures three of these new PGPs known as H5, PGP4 and Resistance Strains. In this project, the research team aimed to identify how they should market BioNorth Solution’s products to the commercial horticulture sector.
Using Collège Boréal’s greenhouse facilities, the research team applied different treatments of fertilizers and of the PGPs to crop seedlings, monitoring their growth and collecting data on the number and weight of fruits or leaves and on any negative side effects. The data allowed the research team to determine the optimal concentration of the new products, their impact on greenhouse crop yield and their effectiveness at reducing the use of agricultural fertilizers. Finally, the research team produced an economic breakeven analysis that will help BioNorth Solutions determine a pricing strategy. If the research is successful, the research team will explore further commercialization opportunities.
Key Words: Crop Yield, Commercialization, Horticulture, Pesticide, Fertilizer, Sustainable Technology, Breakeven Analysis
Project Manager: Josée Latulippe
Partner Organization: Association francophone à l’éducation des services à l’enfance de l’Ontario (Aféseo)
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: Spring 2020 to Spring 2022
This project will identify the best practices for mitigating the negative effects of social distancing and professional and cultural isolation in the early childhood education sector in Francophone Ontario due to the COVID-19 pandemic and, indirectly, contribute to the retention of personnel in the sector. Just like social isolation, professional and cultural isolation can also have harmful impacts on the health of workers and consequently, on the health of organizations themselves. Using a mixed method evaluation, the research team is studying the effectiveness of virtual professional learning communities as a strategy to mitigate the negative impacts of social distancing and professional and cultural isolation.
Among the expected outcomes of the project is the implementation of best practices in the field of early childhood education that could also be adapted to other sectors and crises. The improvement in the well-being, sense of belonging, motivation and engagement of these professionals will also help with retention in a sector that was already facing a labour shortage pre-COVID-19.
Key Words: Early Childhood, Francophone Ontario, COVID-19, Pandemic, Social Distancing, Professional Isolation, Cultural Isolation, Retention, Virtual Community
Project Manager: Kuny Laurin
Student Research Assistant: André Tellier
Partner Organization: Borealis Fresh Farms Inc.
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: January 2020 to June 2020

Innovative forms of indoor farming, such as vertical farming (i.e., growing crops in vertically stacked layers), allows Northern Ontario farms like Borealis Fresh Farms Inc. (BFFI) to meet the year-round demand for local produce. BFFI use zip tower technologies and has faced labour and technical efficiency challenges related to its lettuce production due to a lack of specialized equipment. To address these challenges, the research team designed and produced a prototype tool to more easily remove used seed plugs from the zip tower and created a wireless humidity monitoring system and a remote data collection system that were installed in the zip towers.
At Collège Boréal, the research team constructed a replication of BBFI’s vertical growing set up, including vertical zip towers, water system, UV lamps and lettuce seed plugs. Then, they developed a prototype of the sensors to monitor the saturation of the water and nutrients; a cloud-based humidity monitoring system that could remotely collect data on the nutrition need of the growing lettuce; and a schematic and prototype for a seed plug extraction tool using both 3D printers and laser cutters. The ability to monitor the crops and easily harvest and replace the plugs should greatly increase yields and workflow efficiency.
Key Words: Indoor farming, Vertical farming, Crop yield, Zip tower, Wireless humidity monitoring, remote data collection, Prototype, Harvesting, Seed plug
Project Manager: Denis Ouimette
Student Research Assistants: Jeremy Roy, Danika Courchesne & Alex Létourneau
Partner Organization: Tooketree Passive Homes
Funding Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: September 2020 to February 2021
Environmental challenges such as that of construction waste are often overlooked in the greening of construction. Innovative infrastructure projects that minimize construction waste through design, such as structural insulated panels, can play a key role in protecting the environment. In collaboration with experts from the Tooketree Passive Homes company, the Collège Boréal research team is designing and developing a new cutting-edge sustainable product: a structural insulated panel called the Eco-Digital Wall. This new product will reduce construction waste and improve the energy efficiency of buildings, all the while reducing overall construction costs.
At Collège Boréal, the research team designed and built a structural insulated panel using various sustainable materials, including an exterior wood finish, open joists, insulation made from ecological wood, a rigid insulation board of plywood sheets and a waterproof varnish. The team then installed a data logging system to track temperature changes and complete structural tests to check in-wall compression, flexibility, shearing, and stress load. With the collected data, the research team conducted a feasibility study to determine if the Eco-Digital Wall can be used by the Canadian construction industry.
Key Words: Green construction, Sustainable infrastructure, Construction waste, Energy Efficiency, Feasibility study, Sustainable materials, Data logging system
Project Manager: Josée Latulipe
Partner Organization: Association francophone à l’éducation des services à l’enfance en Ontario (Francophone Association for Children’s Services Education in Ontario)
Granting Agency: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Duration: spring 2020 to autumn 2021
The vitality of Francophone communities in Ontario depends on access to high-quality French-language services, as well as the ability and willingness of parents to transmit the cultural identity to their children. Early childhood is a pivotal moment in the identity-building process for Francophones in a minority setting, a key mechanism for ensuring the vitality of their communities. As part of this project, the research team aims to create an effective training model for transmitting Francophone culture in early childhood to professionals, parents and children.
The model will be developed and evaluated in collaboration with the partner, the Association francophone à l’éducation des services à l’enfance en Ontario. More specifically, the program aims to 1) make early childhood professionals aware of the importance of language planning, support their own identity building and improve their practices in this regard; 2) make parents aware of the importance of appropriating the Francophone language and cultures in order to support their role as a cultural facilitator for their children; and 3) promote identity building among young children and, in the long term, their language skills and their ability to learn in French. The data will come from various sources, including children, parents, early childhood professionals, Collège Boréal students participating in the project, as well as teachers and trainers.
Key Words: Francophone Minority Communities, Identity-Building, Language Planning, Language Skills

Testimony
Being part of an applied research project allowed me to broaden my knowledge. I now better understand the role that agricultural workers play in ensuring that the food consumed by the community is safe.
Cora Long ― Agricultural Techniques
Resources and Documents
Your filters did not return any results.
Commercialization of Intellectual Property Policy Statement
The Province of Ontario issued its Commercialization Mandate Policy Framework in early 2022. The objective of Ontario’s Commercialization Mandate Policy Framework is to harness the intellectual property generated with the institution’s resources to achieve Ontario’s goal of ensuring that made-in-Ontario innovations benefit Ontarians.
Follow the link for the full statement: Commercialization of Intellectual Property Policy Statement
Collège Boréal is an innovative educational, cultural and community hub serving Ontario’s Francophone population. Its goal is to produce a highly qualified bilingual workforce that is engaged in French-speaking communities and contributes to the economic, social and cultural vitality of the province and the country. Visible and recognized, Collège Boréal enriches communities through the quality of its training and personalized services at its seven campuses and 37 sites in 26 communities across the province.
Newly formed in 2019, Research & Innvoation Boréal continues to innovate in order to remain a competitive provincial and national leader in applied research. Collège Boréal remains on the lookout for emerging research areas and themes and positions itself as a leader in the communities it serves, placing particular importance on collaboration with its communities and multi-sectoral research teams. Collège Boréal develops research partnerships with businesses, governments and communities to address their needs and current societal challenges. We work closely with small and medium-sized enterprises in our regions to provide innovative solutions to the challenges they face. Research projects allow us to jointly develop expertise in research and education for our students. They are at the heart of our research projects. By participating, they benefit from experiential learning opportunities, in-depth training in their field of study and exposure to future employers.
Institutional Research Data Management Strategy
In March 2021, the three federal research funding agencies (i.e., the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC)) launched the Tri-Agency Policy on Research Data Management. This policy promotes research data management and data stewardship practices among Canadian researchers. To this end, Canadian postsecondary institutions were asked to develop their own research data management (RDM) strategies and share them publicly on their websites.
Follow the link to access the full strategy (French only): Institutional Research Data Management Strategy
Our Team

Jean Pierre Kapongo (PhD.)
-
For over twenty years, Jean Pierre Kapongo has been conducting in vitro and in situ research projects focusing on plant production and protection. His aim is to preserve biodiversity and the environment while increasing agricultural yields. His research played a significant role in the development of entomovection, a technology used by the Canadian company Bee Vectoring Technology (BVT) and by North American farmers since 2009. As author and co-author of several scientific articles and chapters in specialized journals, he is particularly interested in reducing the use of chemical pesticides in agriculture and promoting new biological technologies for sustainable agricultural production.
At Collège Boréal, Mr. Kapongo directed and supervised several research projects focusing on the application of new techniques and trends in the production and protection of strawberry, oat and plant crops under sheltered conditions. The main aim of these projects was to improve crop yields while preserving biodiversity, ecosystems and the environment.

Kuny Laurin
-
Since the beginning, Kuny has been involved in research projects at Collège Boréal as an expert in industrial design, manufacturing, automation, electronics and programming. His career path has been marked by a constant passion for innovation and creation. One of his achievements is the Smart Windmill Controller (SWC), a project entirely developed and designed at Collège Boréal. This intelligent controller manages the mechanical power of the wind to charge and regulate current for batteries. Another fascinating project he was involved in was the development of adjustable racks for strawberry cultivation. Putting his design and manufacturing skills to good use, he participated in the complete design of the system at Collège Boréal.
His career at Boréal has been marked by fruitful collaborations and concrete achievements, testifying to his expertise in industrial design, manufacturing and technology. His ongoing involvement in innovative projects reflects his passion for research and development, and he is determined to pursue this path in order to actively contribute to the advancement of science and technology.

Marc Hébert, R.P.F.
-
Marc hails from the city of Greater Sudbury and has lived through the dramatic changes to the city's forest environment since the 1980s. Rehabilitation of the forests devastated by the region's mining activities is world-renowned, and part of its history.
This history forged his desire to contribute to the rehabilitation of the region's acidified soils, through the use of wood ash, a bioproduct of the forestry industry. Since 2013, Marc has coordinated six research projects on the use of wood ash to improve acidified and nutrient-poor soil remediation techniques.

Olivia Baudet
- For over 6 years, Olivia has been involved in environmental projects run by the Collège and its partners. Specializing in aquaculture, forestry, and agriculture, she has worked on a number of projects, including a feasibility study on the commercial farming of lake whitefish, the economic potential of plant growth activators, the use of industrial residues for environmental rehabilitation, and the evaluation of the effectiveness of symbiotic cultures of three complementary native species.
Research Week

Useful Links
Useful Links

